Digital Competence of Educators
Last month the European Commission published the report European Framework for the Digital Competence of Educators: DigCompEdu. This report presents a common European Framework for the Digital Competence of Educators (DigCompEdu). The DigCompEdu framework is directed towards educators at all levels of education, from early childhood to higher education and non-formal learning contexts. It can help to guide policy and to adapt training programmes (such as BKO/UTQ).
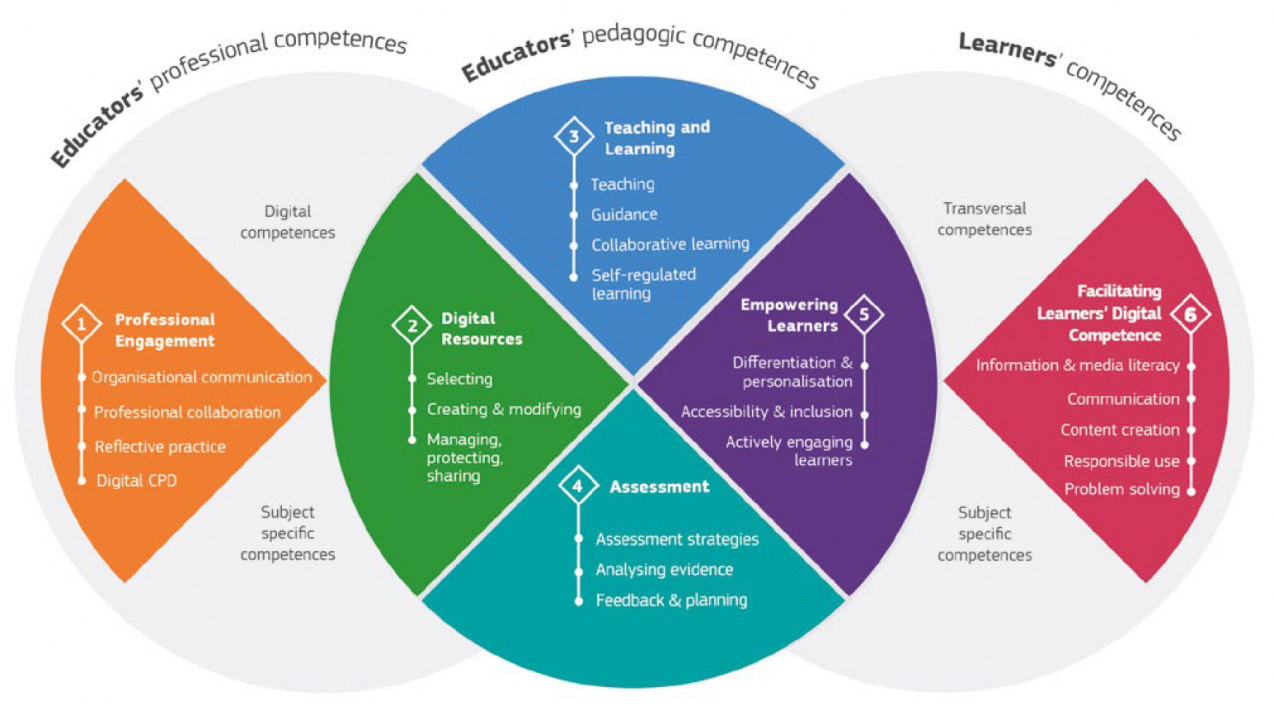
The DigCompEdu framework distinguishes six different areas with total 22 competences:
- Area 1: Professional Engagement
Using digital technologies for communication, collaboration and professional development. - Area 2: Digital Resources
Sourcing, creating and sharing digital resources. - Area 3: Teaching and Learning
Managing and orchestrating the use of digital technologies in teaching and learning. - Area 4: Assessment
Using digital technologies and strategies to enhance assessment. - Area 5: Empowering Learners
Using digital technologies to enhance inclusion, personalisation and learners’ active engagement. - Area 6: Facilitating Learners’ Digital Competence
Enabling learners to creatively and responsibly use digital technologies for information, communication, content creation, wellbeing and problem-solving.
Professional Engagement
An educator should not only be able to use digital technologies for teaching, but also for their professional engagement, such interactions with colleagues and continuous professional development.

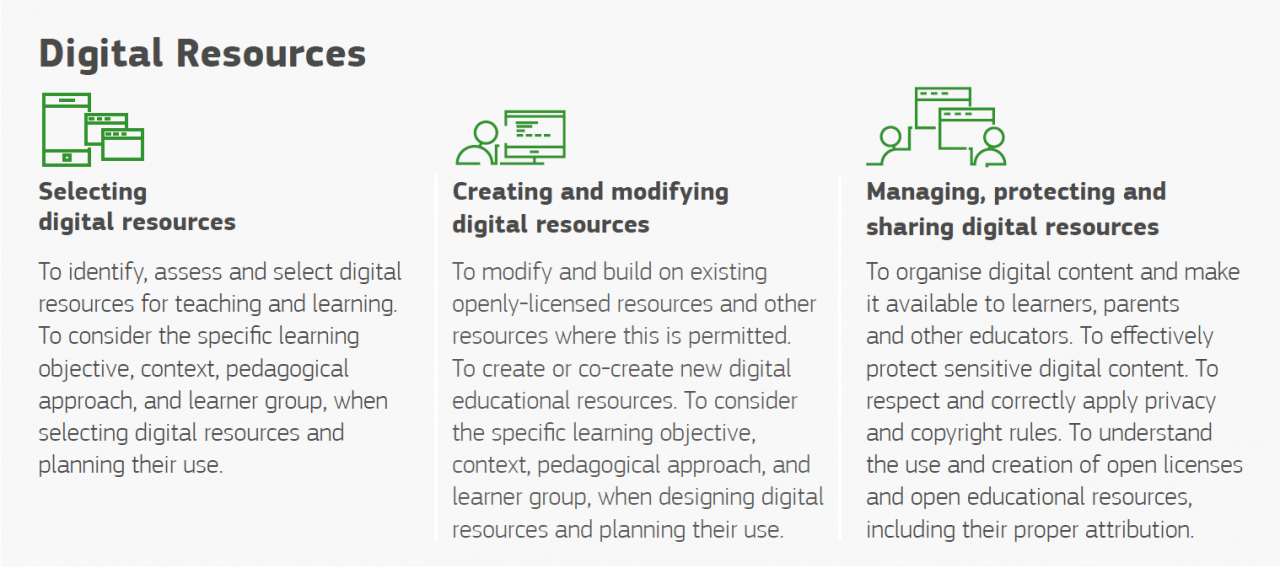
Digital Resources
There are so many great resources available online that can be used for teaching. As an educator you should be able to select, create and modify digital resources. You should know the copyright rules when using, modifying and sharing resources, and protect sensitive content and data, such as digital exams or students’ grades.
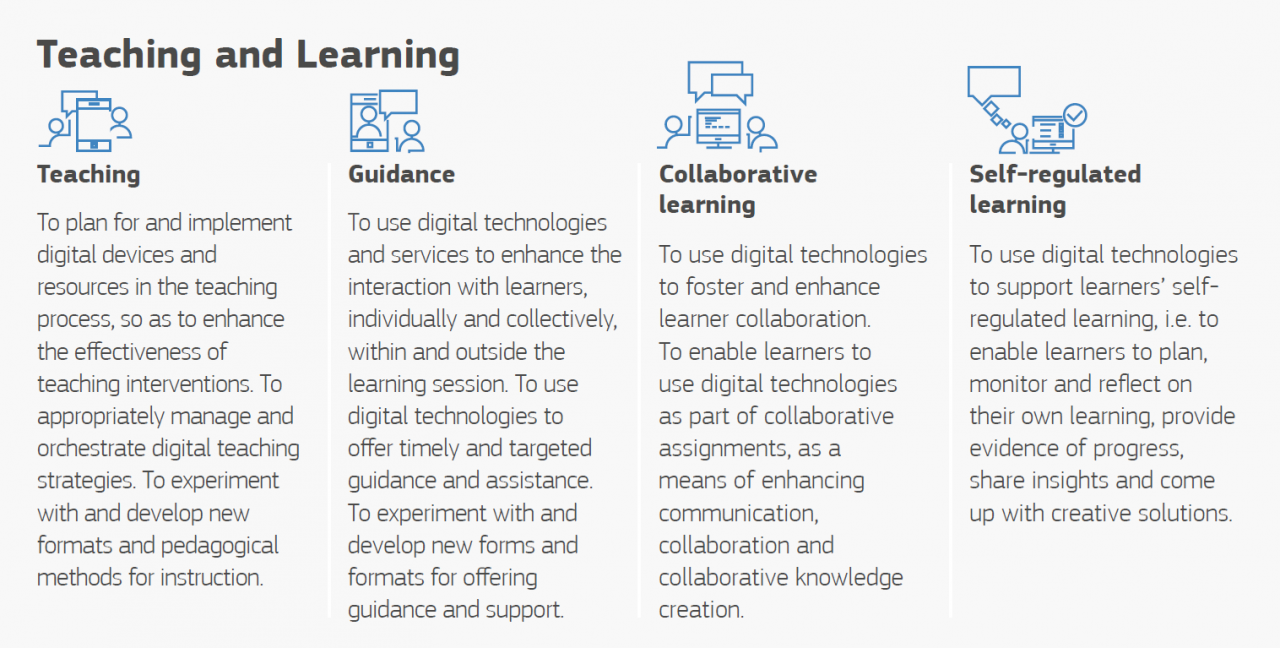
Teaching and Learning
This is the core area of competencies of the framework. Digital technologies can enhance and improve teaching and learners, but is currently often under used because of the digital competency of an educator.
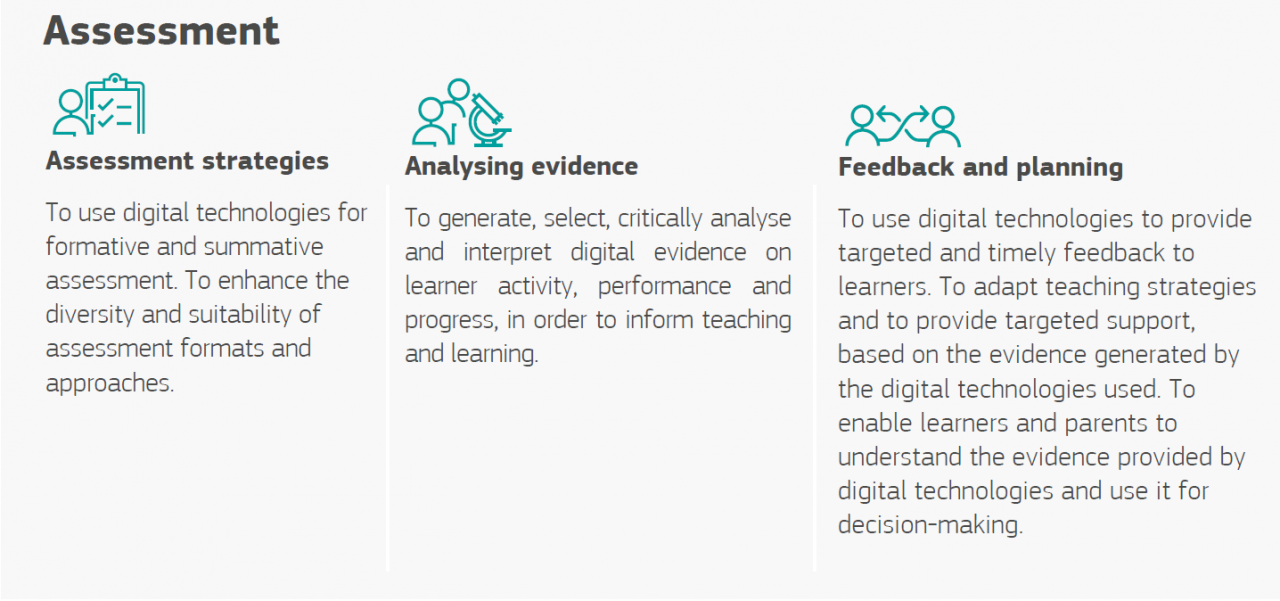
Assessment
Digital technologies offer great opportunities to facilitate innovative assessment approaches. We really can move away from the 3 hour written exams.
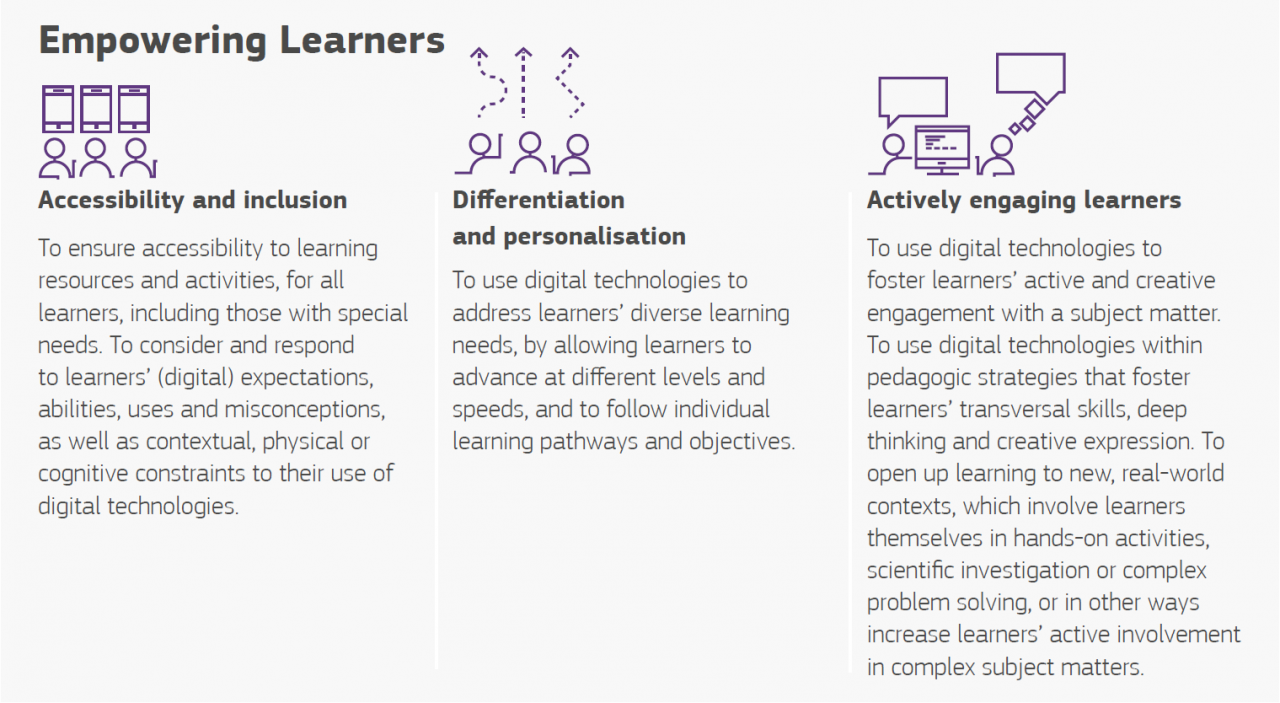
Empowering Learners
Digital technologies can contribute to supporting classroom differentiation and personalised education by offering learning activities adapted to each individual learner’s level of competence, interests and learning needs. But be aware to ensure accessibility for all learners.
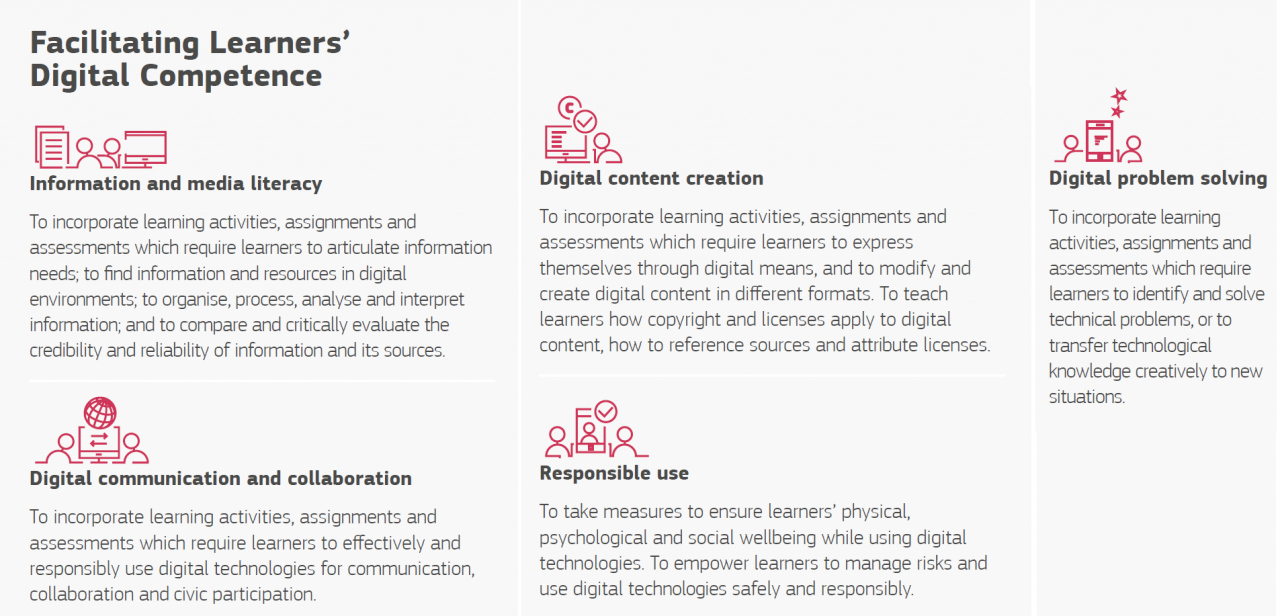
Facilitating Learners' Digital Competence
As an educator you should be able to facilitate the development of learners' digital competences.
Conclusion
The report is a must read for educators and educators of educators. The report also describes more in depth what it means for education to be digitally competent. It als has a useful list of typical activities per competence.
Reference
- Redecker, C. European Framework for the Digital Competence of Educators: DigCompEdu. Punie, Y. (ed). EUR 28775 EN. Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg, 2017, ISBN 978-92-79-73494-6, doi:10.2760/159770, JRC107466
- All images are screenshots from the report, some are altered for better display
No feedback yet
Form is loading...